Unlocking Remote IoT: What It Is & How It Works!
What exactly isRemoteIoT, and why is it rapidly reshaping the landscape of technological innovation? RemoteIoT represents a fundamental shift in how we interact with, manage, and derive value from the Internet of Things (IoT) devices, enabling a new era of accessibility, control, and operational efficiency. This concept is not just a buzzword; it's a paradigm shift in how we perceive the capabilities and potential of interconnected devices.
The core principle behind RemoteIoT is the ability to access, control, and monitor IoT devices from a distance. This capability is crucial in a world where these devices are deployed across diverse and often geographically dispersed locations. Imagine sensors embedded in remote agricultural fields, industrial machinery operating in factories, or even smart home appliances in a vacation home. The capacity to interact with these devices remotely opens up a myriad of opportunities, from optimizing operational performance to improving safety and security, and enhancing data-driven decision-making.
The evolution of RemoteIoT is intricately linked to advancements in several key technologies. The proliferation of robust and secure communication networks, including cellular, Wi-Fi, and satellite connections, provides the necessary infrastructure for reliable data transmission. Cloud computing platforms play a vital role, offering the processing power, storage capacity, and analytical tools needed to manage the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices. Furthermore, edge computing, which brings processing closer to the source of data, is becoming increasingly important, especially in scenarios where low latency and real-time responsiveness are critical.
RemoteIoT is not a monolithic entity; it encompasses a range of functionalities tailored to meet specific needs. Remote monitoring allows users to track the status and performance of devices in real time, enabling early detection of potential issues and proactive maintenance. Remote control provides the ability to adjust device settings, initiate actions, and manage functionalities from a distance. Remote diagnostics enables the identification and resolution of problems without the need for on-site intervention, reducing downtime and associated costs. Remote configuration allows for the effortless setup and modification of device parameters, ensuring optimal performance and adaptability to changing conditions. Finally, over-the-air (OTA) updates facilitate the seamless deployment of software updates, bug fixes, and new features, enhancing security and extending the lifespan of devices.
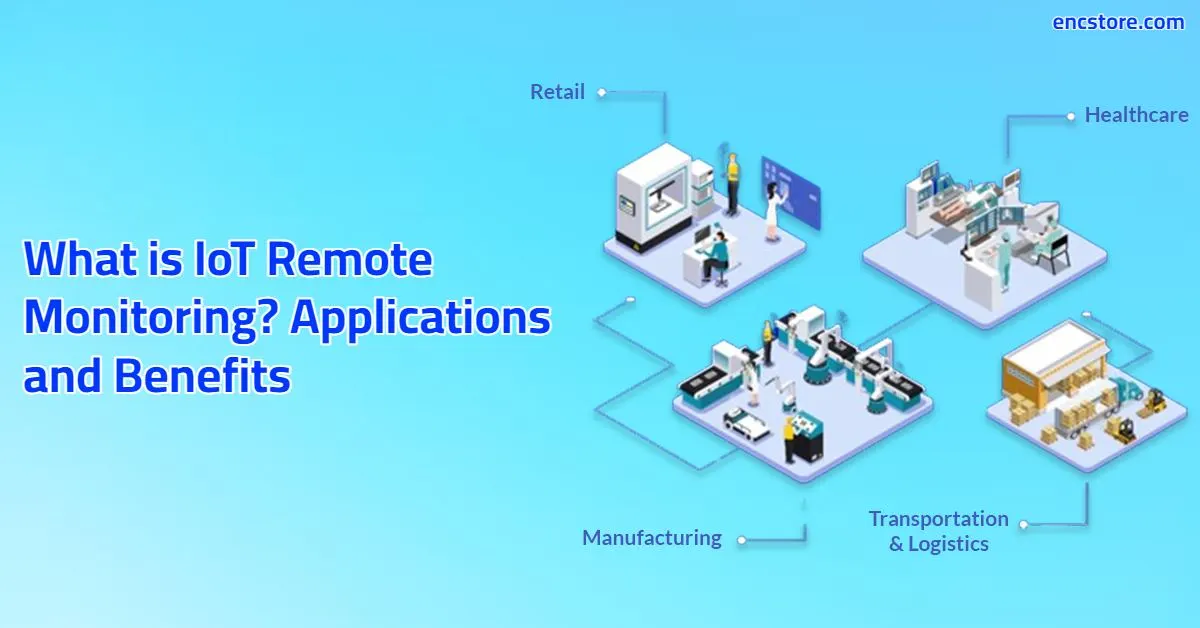
The integration of these functionalities contributes to various advantages across different industries. In manufacturing, RemoteIoT facilitates predictive maintenance, enabling manufacturers to anticipate equipment failures and schedule maintenance proactively, reducing downtime and operational costs. In agriculture, it supports precision farming, allowing farmers to monitor environmental conditions, optimize irrigation, and manage resources more efficiently. In healthcare, remote patient monitoring allows healthcare providers to monitor patients' vital signs and health conditions remotely, improving patient care and reducing the need for hospital visits. In the transportation sector, RemoteIoT helps in fleet management, allowing companies to track vehicles, monitor driver behavior, and optimize routes. The possibilities are truly expansive, and we are only beginning to fully appreciate the transformative power of RemoteIoT across various sectors.
The security considerations of RemoteIoT are paramount. As devices are increasingly connected and accessible remotely, the attack surface expands, making it crucial to implement robust security measures. These include encryption, authentication, access control, and regular security audits to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyberattacks. The implementation of strong security protocols is not merely a technical requirement; it is a fundamental principle of responsible RemoteIoT deployment, ensuring the trust and confidence of users and stakeholders.
Several examples of practical applications illustrate the significance of RemoteIoT. In the realm of smart cities, RemoteIoT solutions are used to monitor traffic flow, manage streetlights, and optimize waste collection, enhancing urban efficiency and sustainability. In the energy sector, RemoteIoT enables smart grid management, optimizing energy distribution, and integrating renewable energy sources. In the retail sector, RemoteIoT is used to monitor inventory levels, manage refrigeration units, and optimize supply chain operations. These tangible applications demonstrate the tangible impact of RemoteIoT and its capacity to drive positive change in numerous aspects of our lives.
Consider the deployment of RemoteIoT solutions in the context of a smart manufacturing plant. Sensors embedded within industrial machines monitor performance metrics such as temperature, vibration, and pressure. This data is transmitted in real-time to a central monitoring system. This system analyzes the data to identify potential issues, such as unusual wear and tear or impending failure. Maintenance personnel can then be notified, and proactive interventions can be scheduled before a breakdown occurs. This preventative approach significantly reduces downtime, optimizes production, and minimizes costly repairs.
In agriculture, RemoteIoT is revolutionizing farming practices. Sensors deployed in fields monitor soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels. Data is transmitted to a central platform where it is analyzed to determine optimal irrigation and fertilization strategies. Farmers can remotely control irrigation systems, adjust fertilizer application rates, and make data-driven decisions to optimize crop yields and conserve resources. This results in higher productivity, reduced water usage, and more sustainable farming practices.
The growth of RemoteIoT is not without its challenges. Interoperability between devices from different manufacturers can be complex. The deployment of large-scale RemoteIoT systems can require significant investment. And the management of the massive volumes of data generated by connected devices requires specialized expertise and infrastructure. These challenges are being addressed through standardization efforts, the development of open-source platforms, and the increasing availability of affordable cloud-based solutions.
The future of RemoteIoT appears bright. Advances in areas such as 5G connectivity, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) are poised to further accelerate its growth. 5G networks provide faster speeds, lower latency, and enhanced connectivity, enabling new RemoteIoT applications and supporting more complex use cases. AI and ML algorithms can be used to analyze the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices, identify patterns, and provide valuable insights for decision-making. These developments are expected to unlock new levels of automation, efficiency, and innovation in the years to come.
The impact of RemoteIoT extends beyond specific industries, shaping our society in profound ways. It facilitates increased resource efficiency, enabling more sustainable practices. It drives innovation, fostering the development of new products and services. It enhances accessibility, improving the lives of people in remote or underserved areas. The transformative power of RemoteIoT is undeniable, and its influence will only continue to grow, transforming how we live, work, and interact with the world around us.
Consider the case of a hypothetical company, "InnovateTech Solutions", specializing in RemoteIoT deployments for the agricultural sector. They design and implement a comprehensive RemoteIoT system for a large-scale farm, encompassing soil moisture sensors, weather stations, and automated irrigation control. Through a user-friendly dashboard, the farm manager can monitor real-time data, adjust irrigation schedules remotely, and receive alerts about potential issues. The system integrates with AI-powered analytics to optimize water usage and predict crop yields. The result? A significant reduction in water consumption, increased crop yields, and enhanced operational efficiency, all thanks to the strategic application of RemoteIoT technology. This example highlights the potential of RemoteIoT to drive tangible benefits across diverse sectors.
The evolution of RemoteIoT is further fueled by the development of new hardware and software tools. Specialized microcontrollers are designed specifically for IoT applications, offering low power consumption, enhanced security features, and robust connectivity options. Cloud platforms provide comprehensive services for managing, analyzing, and visualizing IoT data. Development tools and software libraries simplify the process of creating and deploying RemoteIoT applications. These advancements are democratizing access to RemoteIoT technology, empowering developers and businesses of all sizes to harness its potential.
Looking to the future, expect RemoteIoT to be even more integrated into our daily lives. Imagine a world where your home appliances, your car, and your city infrastructure are seamlessly connected and managed remotely. The potential for innovation is limitless. The key to unlocking the full potential of RemoteIoT lies in its responsible and ethical deployment. This includes prioritizing security, privacy, and interoperability, ensuring that the technology benefits all stakeholders. As RemoteIoT continues to evolve, it is vital to address the challenges and embrace the opportunities that it presents to create a more connected, efficient, and sustainable future. The ongoing dialogue about this technology, including considerations of its impacts, helps drive responsible development.